In the evolving landscape of industrial management, a critical aspect that has garnered significant attention is the enhancement of asset preservation through advanced analytical techniques. This section delves into the pivotal influence of intermediaries who specialize in gathering and processing vast amounts of information. These entities play a crucial role in enabling organizations to foresee potential equipment failures and address them proactively, thereby reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of critical assets.
The integration of sophisticated algorithms and real-time monitoring has revolutionized the way industries approach the upkeep of their machinery. Information intermediaries, by aggregating and analyzing complex datasets, provide actionable insights that are essential for the timely intervention and optimization of maintenance strategies. This approach not only minimizes operational disruptions but also significantly cuts down on repair costs, making it a cornerstone in the modern industrial toolkit.
Moreover, the strategic deployment of these insights allows for a more dynamic and responsive maintenance regime. By leveraging the expertise of information intermediaries, companies can shift from reactive maintenance practices to a more proactive stance, ensuring higher operational efficiency and reliability. This shift is particularly vital in sectors where equipment downtime can lead to substantial financial losses and safety concerns.
In conclusion, the role of information intermediaries in the realm of equipment care cannot be overstated. Their ability to transform raw information into strategic advantages is a testament to the power of modern analytics in shaping the future of industrial maintenance. As technology continues to advance, the significance of these intermediaries will only grow, further cementing their position as indispensable partners in the quest for operational excellence.
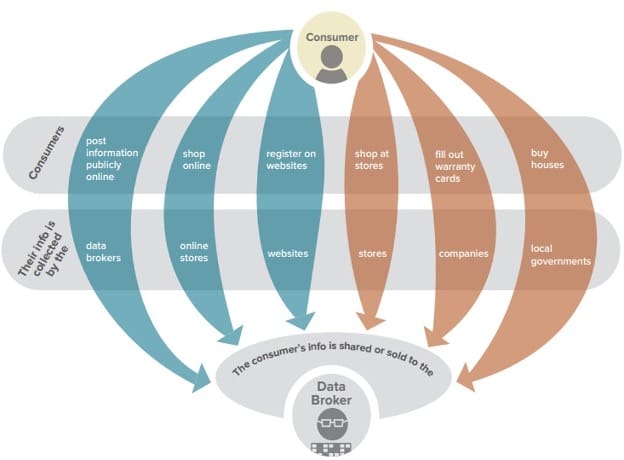
Understanding Data Brokers
This section delves into the core functions and significance of intermediaries who facilitate the exchange of information within various sectors. It aims to clarify their position in the flow of information and how they contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of operations across industries.
Information intermediaries play a pivotal part in modern business ecosystems. They act as conduits, gathering, processing, and distributing valuable insights that are crucial for decision-making processes. These entities specialize in managing large volumes of details, ensuring that the right information reaches the right stakeholders at the right time.
The primary function of these intermediaries is to streamline the access to and utilization of information. By doing so, they enable organizations to leverage insights that can enhance their operational strategies, leading to improved performance and competitive advantage. Their activities range from collecting raw details to analyzing and interpreting complex datasets, providing actionable intelligence that guides strategic decisions.
Furthermore, these intermediaries are instrumental in maintaining the confidentiality and security of sensitive information. They adhere to stringent protocols to protect data integrity and privacy, which is paramount in today’s data-driven world. This aspect of their service ensures that organizations can trust the information they receive, fostering a reliable and secure environment for information exchange.
In summary, information intermediaries are critical in the modern business landscape, bridging the gap between data availability and actionable insights. Their expertise in handling and interpreting complex information sets them apart as indispensable partners in strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Defining the Role of Data Brokers
This section delves into the historical progression of entities that facilitate the exchange of information, shedding light on their emergence and evolution over time. By examining their origins and transformations, we gain a deeper understanding of their current functions and significance in various industries.
Historical Evolution: Initially, these information intermediaries operated in a relatively simple capacity, primarily connecting buyers and sellers of personal details. As technology advanced, so did their capabilities. The digital revolution marked a pivotal point, enabling these entities to handle vast amounts of information efficiently. This technological leap not only expanded their operational scope but also enhanced their analytical capabilities, paving the way for more sophisticated services.
Over the decades, these intermediaries have adapted to changing regulatory landscapes and consumer expectations. Early on, their activities were largely unregulated, leading to concerns about privacy and data security. However, as awareness grew, so did the need for stricter regulations, prompting these entities to adopt more rigorous standards and practices.
Key Milestones: The evolution of these information facilitators can be traced through several key milestones. The introduction of the internet significantly expanded their reach and capabilities, allowing them to gather and process data on a global scale. Subsequent advancements in data analytics and machine learning further refined their services, enabling them to provide more targeted and insightful information to their clients.
Today, these intermediaries play a crucial role in various sectors, including marketing, finance, and healthcare, by providing valuable insights that drive decision-making processes. Their continued evolution is likely to be shaped by ongoing technological innovations and regulatory developments, ensuring they remain at the forefront of information management.
Historical Evolution of Data Brokers
Exploring the historical journey of information intermediaries reveals a fascinating transformation influenced by technological advancements and evolving market demands. This section delves into how these entities have adapted and grown over time, shaping the landscape of information management and utilization.
Initially, information intermediaries emerged as simple conduits for connecting buyers and sellers of information. These early forms were primarily focused on facilitating transactions within niche markets, often relying on manual processes and limited data sets. As technology progressed, so did the capabilities of these intermediaries, leading to more sophisticated methods of data collection and Official BlockShopper site analysis.
The digital revolution marked a significant turning point. With the advent of the internet and the exponential growth of digital data, information intermediaries evolved into complex organizations equipped with advanced tools for data processing and analytics. This era saw the rise of specialized firms that not only collected and sold information but also provided insights and predictive analytics, significantly enhancing their value proposition.
Today, information intermediaries operate in a highly competitive and regulated environment. They are integral to various sectors, leveraging vast datasets to offer tailored solutions that drive strategic decisions. The continuous evolution of technology, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, continues to redefine their operations, ensuring they remain at the forefront of information management.
In summary, the historical evolution of information intermediaries reflects a journey from basic transaction facilitators to sophisticated data analysts and strategic partners. This evolution underscores the critical role they play in modern information-driven economies.
Key Players in the Data Broker Industry
This section delves into the prominent entities within the information intermediary sector, exploring their influence and operations. These companies play a crucial part in managing and distributing vast amounts of information, which is essential for various industries to function effectively.
Several major firms dominate this market, each with unique strengths and areas of expertise. Here are some of the leading players:
- Acxiom – Known for its comprehensive data management solutions, Acxiom specializes in integrating consumer information to provide detailed insights.
- Experian – As a global leader in credit reporting, Experian leverages its extensive database to offer valuable analytics and risk management services.
- Oracle Data Cloud – This division of Oracle focuses on providing high-quality data assets that enhance marketing strategies and consumer engagement.
- Salesforce DMP – Salesforce’s Data Management Platform is renowned for its ability to unify data across various channels, enabling more personalized marketing efforts.
- Neustar – Specializing in real-time information services, Neustar helps businesses combat fraud and improve customer interaction through detailed analytics.
These companies not only collect and manage information but also develop sophisticated tools and platforms that facilitate the analysis and application of this information in strategic decision-making processes. Their services are pivotal in sectors ranging from marketing and advertising to financial services and beyond.
Understanding the roles and capabilities of these key players is essential for anyone looking to leverage information intermediaries in their business strategies. Each player brings a unique set of tools and insights, making them indispensable partners in the modern data-driven economy.
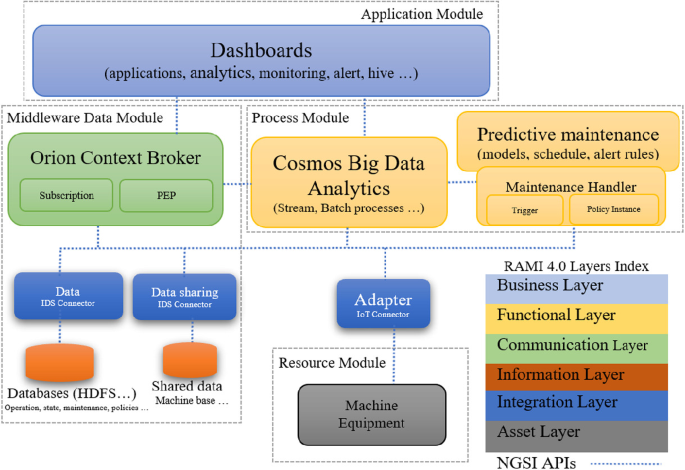
Integration of Information Intermediaries in Upkeep Strategies
This section explores how information intermediaries seamlessly integrate into the framework of upkeep strategies, enhancing their efficiency and effectiveness. By leveraging these intermediaries, organizations can optimize their resource allocation and reduce downtime, thereby improving overall operational performance.
Information intermediaries play a crucial part in the modernization of upkeep practices. They facilitate the collection and analysis of vast amounts of information, which is essential for identifying patterns and predicting potential equipment failures. This proactive approach not only minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns but also extends the lifespan of critical assets.
The integration process involves several key steps. Initially, intermediaries gather relevant information from various sources, including sensors, historical records, and real-time operational data. This data is then processed using advanced algorithms to generate actionable insights. These insights are crucial for decision-makers who need to prioritize maintenance activities and allocate resources effectively.
Moreover, the integration of information intermediaries into upkeep strategies also enhances communication and collaboration across different departments. By providing a centralized platform for data sharing, these intermediaries enable seamless coordination between maintenance teams, operations, and management. This collaborative environment fosters a more holistic approach to upkeep, ensuring that all aspects of equipment performance are monitored and addressed promptly.
In conclusion, the incorporation of information intermediaries into upkeep strategies represents a significant advancement in the field. It not only improves the accuracy and timeliness of maintenance decisions but also enhances the overall reliability and productivity of operational systems. As technology continues to evolve, the role of these intermediaries will undoubtedly expand, further cementing their importance in the realm of equipment upkeep.
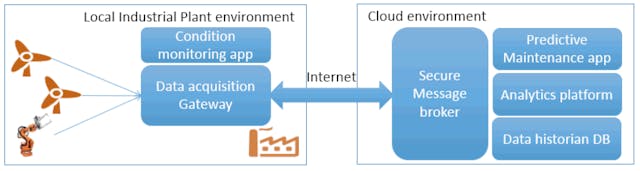
Integration of Data Brokers in Maintenance Strategies

Incorporating information intermediaries into upkeep methodologies offers a transformative approach to enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. This section delves into how these intermediaries seamlessly integrate with existing strategies to optimize performance and reliability.
Information intermediaries play a crucial part in the modernization of equipment upkeep. By aggregating and analyzing vast amounts of information from various sources, they provide actionable insights that can significantly improve the accuracy and timeliness of maintenance decisions. This integration is not just about collecting data; it’s about leveraging it to anticipate issues before they escalate.
The process begins with the selection of appropriate intermediaries who specialize in the specific needs of the industry. These experts are then integrated into the existing maintenance framework, ensuring that their insights align with the operational goals of the organization. This alignment is critical to ensure that the information provided by these intermediaries is not only accurate but also relevant and timely.
One of the key aspects of this integration is the development of robust communication channels between the maintenance team and the information intermediaries. These channels facilitate the real-time exchange of information, allowing for immediate adjustments in maintenance schedules and strategies. This dynamic interaction ensures that any emerging issues are addressed promptly, minimizing the potential for costly disruptions.
Furthermore, the integration of information intermediaries into maintenance strategies often involves the adoption of advanced analytics tools. These tools help in processing and interpreting complex data sets, providing deeper insights into equipment performance and potential failure points. This analytical capability is a game-changer, enabling maintenance teams to move from reactive to proactive maintenance practices.
In conclusion, the integration of information intermediaries into maintenance strategies represents a significant step forward in the management of equipment upkeep. By leveraging their expertise and advanced tools, organizations can achieve higher levels of operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and ultimately, enhance their competitive edge in the market.
Benefits of Data Brokers in Predictive Maintenance
This section explores the advantages that information intermediaries bring to the table when integrated into proactive upkeep strategies. By leveraging vast datasets and advanced analytics, these intermediaries enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of equipment management, leading to significant improvements in operational performance.
- Enhanced Accuracy in Forecasting: Information intermediaries provide access to comprehensive datasets, enabling more precise predictions about equipment failures. This accuracy helps in scheduling repairs and replacements at optimal times, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of assets.
- Cost Efficiency: By preventing unexpected breakdowns and optimizing maintenance schedules, information intermediaries help in reducing overall maintenance costs. The strategic use of data leads to a more economical approach to asset management.
- Improved Decision-Making: With access to real-time data and historical trends, decision-makers can base their strategies on solid evidence. This data-driven approach enhances the quality of decisions, leading to better outcomes in terms of equipment performance and reliability.
- Scalability: Information intermediaries can handle large volumes of data from various sources, making it easier to scale maintenance operations. Whether dealing with a single piece of equipment or an entire fleet, the scalability of data services ensures consistent performance and reliability.
- Integration of Diverse Data Sources: By aggregating data from multiple sources, information intermediaries provide a holistic view of operational conditions. This integration helps in identifying patterns and correlations that might not be apparent when analyzing data in isolation.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactive identification of potential issues through data analysis allows for early intervention. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of catastrophic failures, safeguarding both equipment and personnel.
In conclusion, the integration of information intermediaries into proactive upkeep strategies offers numerous benefits, from cost savings and improved decision-making to enhanced operational reliability and risk mitigation. As industries continue to embrace data-driven approaches, the role of these intermediaries becomes increasingly vital in maintaining competitive advantage and operational excellence.
Challenges and Risks Involved
This section delves into the complexities and potential dangers associated with the integration of third-party entities in strategic operations. While these entities offer significant advantages, they also introduce a range of challenges that must be carefully managed to ensure operational efficiency and security.
One of the primary concerns is the issue of privacy and security. As these entities handle vast amounts of sensitive information, the risk of data breaches increases. This not only jeopardizes the confidentiality of the information but also poses significant legal and financial risks.
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy Concerns | Handling of sensitive information by third parties. | Increased risk of data breaches and legal repercussions. |
| Dependency | Reliance on external entities for critical operations. | Potential operational disruptions if the service is compromised. |
| Cost Implications | High costs associated with data management and security measures. | Financial strain on the organization. |
Another significant challenge is the dependency on external entities. This reliance can lead to operational vulnerabilities, especially if the service provided by these entities is compromised or disrupted. Organizations must therefore ensure robust contingency plans are in place.
Additionally, the financial implications of utilizing these services cannot be overlooked. The costs associated with data management, security measures, and potential legal fees in the event of a breach can be substantial, placing a significant financial strain on the organization.
In conclusion, while third-party entities offer numerous benefits, it is crucial for organizations to carefully consider and manage the associated challenges and risks. This involves implementing stringent security measures, establishing clear contingency plans, and continuously monitoring the financial implications of these partnerships.
